Mammography
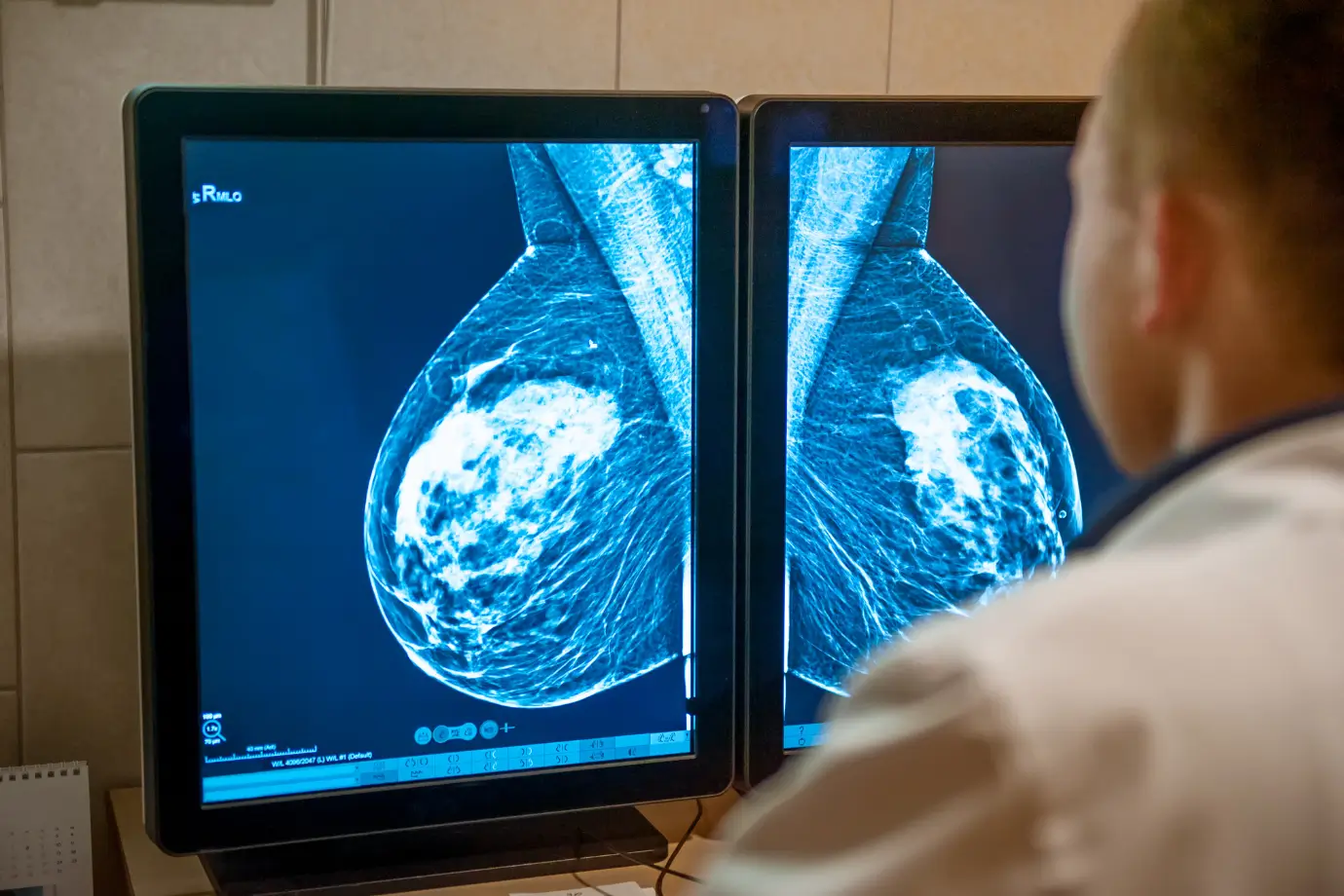
Mammography is a well-established screening and diagnostic tool used to evaluate breast tissue for the possible presence of cancer through the use of low-dose X-rays.
The goal of mammography is to aid in the early detection of breast changes and doing so, improve prognosis.
We utilize tomosynthesis with our mammograms, which is an advanced form of mammography providing thin slice evaluation, improving detection rates, and reducing the need to perform additional mammographic views.
All our mammograms are followed by an ultrasound examination to allow for further analysis and, if necessary, lesion characterization.
All mammograms and ultrasounds are performed by trained mammographers and reviewed by a radiologist.
We follow international guidelines and recommend an annual mammogram from age 40. Rarely, in patients at higher risk, earlier screening mammograms might be indicated.
If a lesion is detected, we offer imaging-guided biopsies, including ultrasound-guided and stereotactic (mammogram) guided biopsies.
If your last mammogram was performed elsewhere, please bring the CD or films along, if available.
Do not wear deodorant, lotion or use talcum powder on the day of examination, as they can cause artefacts, limiting evaluation.
You should inform the mammographer if there is any chance you might be pregnant.